Types of Social Security pensions

The Social Security system offers more than one type of so-called “pension” in addition to the classic retirement pension.
In fact, the system is designed to cover different needs and situations, of which retirement is just one example. It does, however, consume the most resources of all the benefits, especially in the case of contributory pensions.
Indeed, the first level of state pensions requires us to differentiate between contributory and non-contributory pensions. From there, each pension can be distinguished according to its purpose.
Contributory and non-contributory pensions
The Social Security offers two basic types of pensions, depending on whether the minimum contributions to the system have been made. These are contributory and non-contributory pensions.
Contributory pensions are related to the payments that workers make to the Social Security and there are certain contribution requirements that must be met to be able to receive them. For example, to access a contributory retirement pension it is necessary to have paid into the system for at least 15 years, two of which must be within the 15 years prior to the time of retirement.
As you can see, this pension is directly linked to the length of time you pay into the system. In addition, when calculating a state retirement pension the amount you have contributed is also taken into account. In other words, how much money you have contributed to the system.
On the other hand, there are non-contributory pensions, which do not depend on contribution periods or payments into the system. These benefits have more of a social welfare-related character.
They are designed to cover the basic needs of anyone who does not have sufficient resources and, consequently, the amount is lower and the requirements for receiving this kind of pension are usually linked to not exceeding a certain income threshold.
Types of contributory pensions
Contributory pensions are the basis of the pension system in Spain and one of the State’s main expenses. So much so that they represent around 11% of the national Gross Domestic Product (GDP):
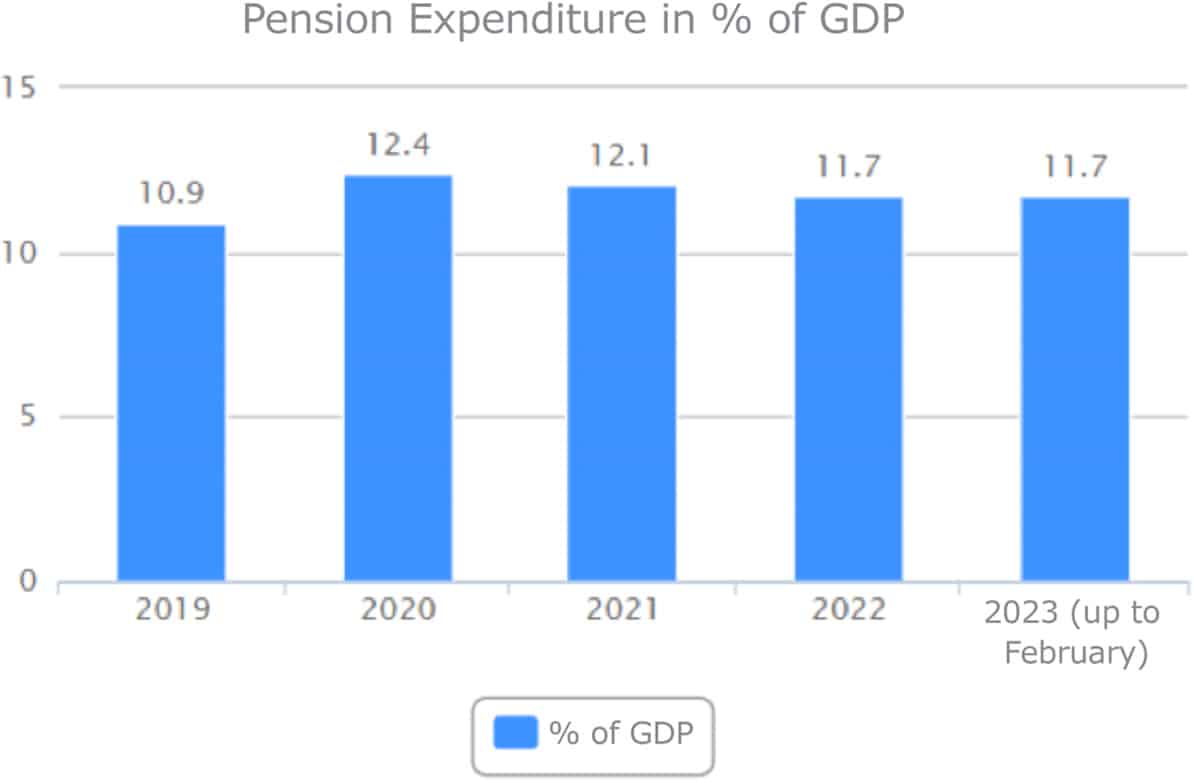
Here, too, there are different types of pensions, although the most important, and the one that involves most expenditure is the retirement pension, both in terms of the number of pensioners and the amounts allocated to it.
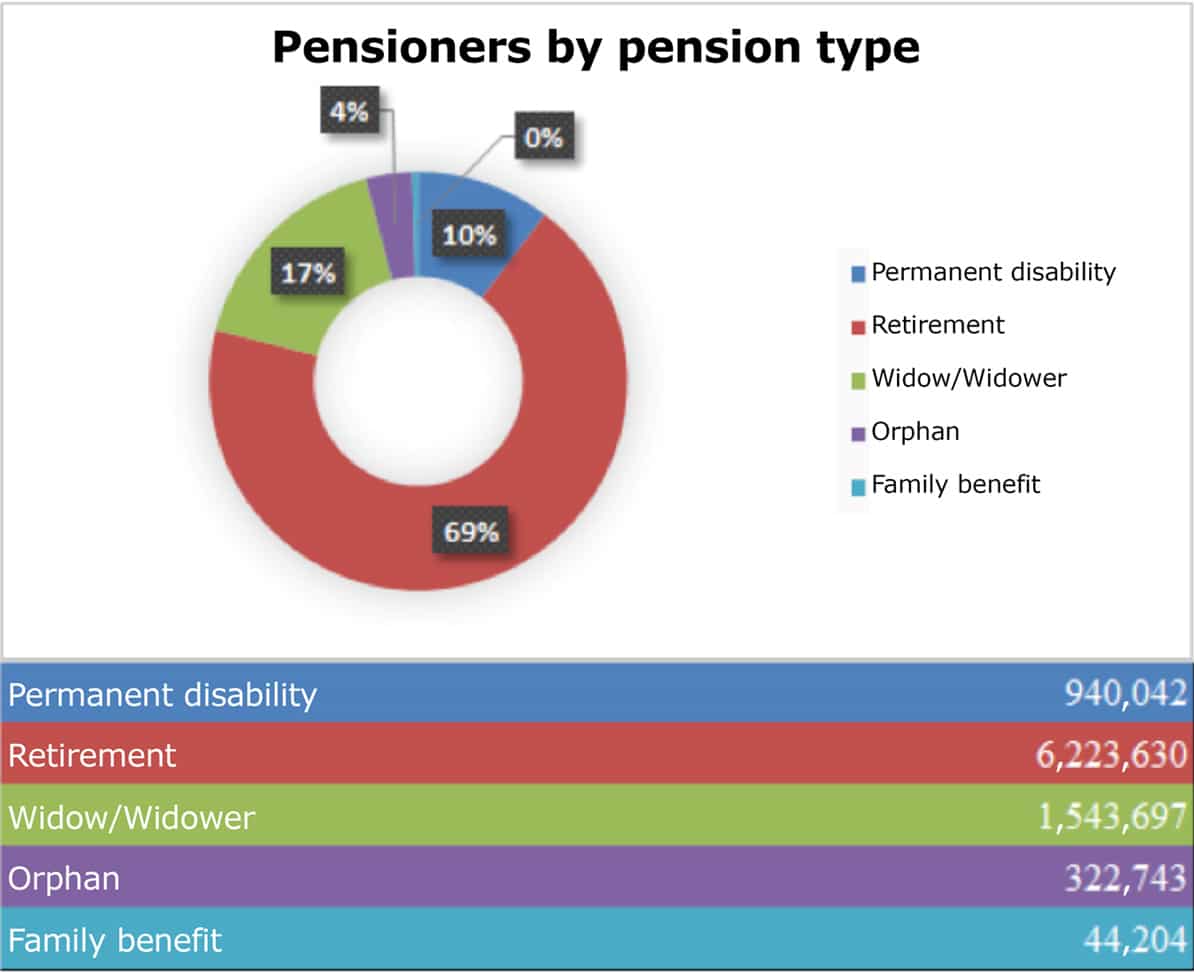
This brief review already gives us an idea of the types of contributory Social Security pensions, which can be summarized as follows:
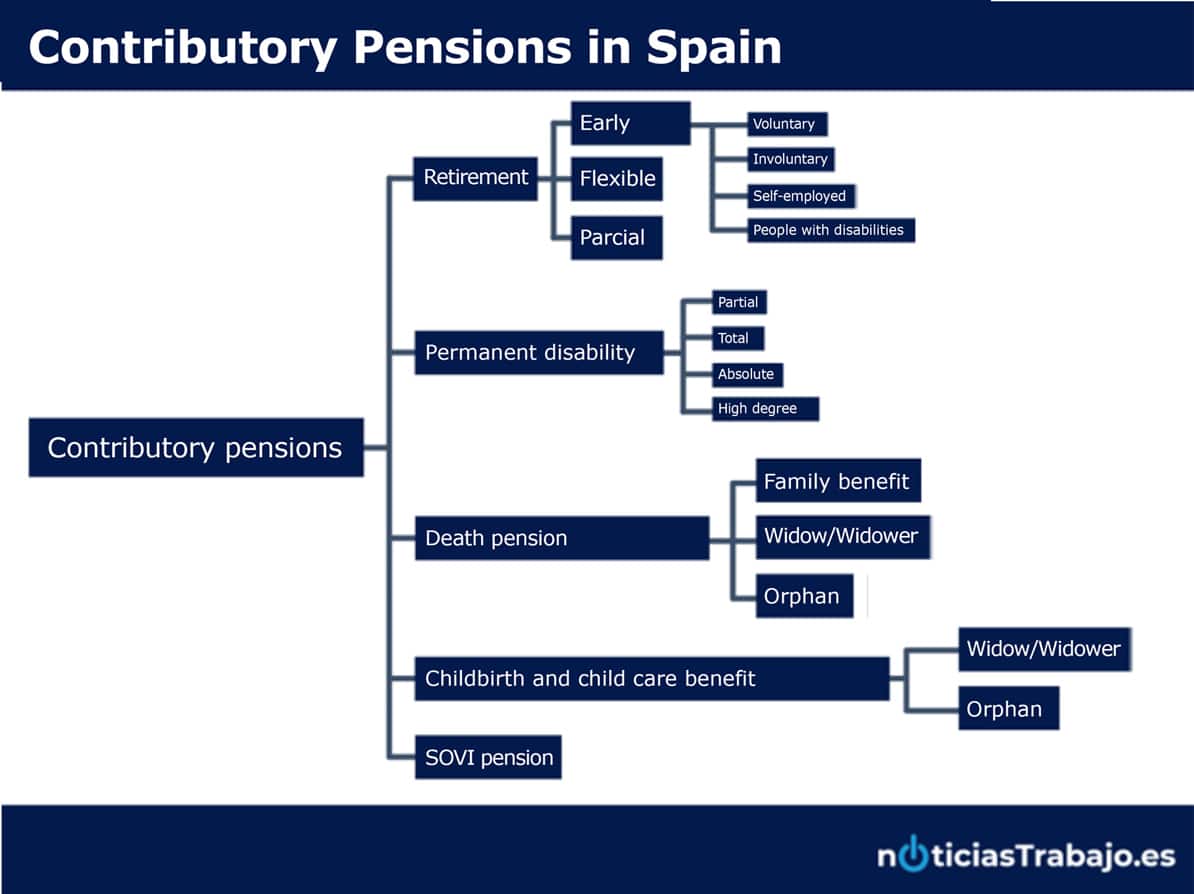
Contributory retirement pension
This is the most important pension and usually the first one we think of when we talk about state pensions.
To be eligible for a retirement pension, it is necessary to have paid into the system for at least 15 years and to have made contributions for at least 2 years in the 15 years prior to the eligibility date. In the case of normal retirement, you must also have reached the legal pensionable age. This could be 65, or an age between 65 and 67, which will depend on the eligibility year and the contribution period, according to the attached table.
| Retirement year | Contribution periods | Age required |
| 2023 | 37 years and 9 months or more | 65 years |
| Less than 37 years and 9 months | 66 years and 4 months | |
| 2024 | 38 years or more | 65 years |
| Less than 38 years | 66 years and 6 months | |
| 2025 | 38 years and 3 months or more | 65 years |
| Less than 38 years and 3 months | 66 years and 8 months | |
| 2026 | 38 years and 6 months or more | 65 years |
| Less than 38 years and 6 months | 66 years and 10 months | |
| A partir de 2027 | 38 years and 6 months or more | 65 years |
| Less than 38 years and 6 months | 67 years |
This age will be progressive and will be 67 in 2027. As of that year, the normal retirement age will be 67, unless at 65 you have completed your contributions (38 years and 6 months ).
It is also possible to take advantage of other retirement modalities and collect a retirement pension. They are the following:
- Early retirement allows you to retire before reaching the normal retirement age. Specifically, it is possible to retire up to 2 years early, or up to 4 years before the normal retirement age, depending on whether you decide to retire early or not, respectively. It is also necessary to prove a contribution period of 35 or 33 years, respectively, depending on the voluntary nature of the early retirement.
This type of retirement involves a reduction in the amount of the pension, which will be greater the earlier the pension is taken.
- Flexible retirement makes it possible to work while you receive your state pension. Very briefly, flexible retirement involves reducing your working hours by between 25% and 50% so that you can work and receive the proportional part of your retirement pension. For example, a person who works half a day and who would be entitled to a pension of 1,200 euros will receive 600 euros from the State.
- Partial retirement, which is similar to the previous one, differs by allowing workers access to their state pension before they reach the legal retirement age.
- Active retirement is where the worker, who at that moment is entitled to 100% of their normal pension if they retire, decides to continue working and receive 50% of their pension. In other words, they get half of their pension, but there are no limits on the type of contract or working day.
Active retirement also applies to self-employed workers who, if they have employees, will be entitled to 100% of their pension.
Contributory death pension
This is the second most typical type of contributory pension and includes the so-called widow’s pension, orphan’s pension, and pension for family members.
The widow’s, or widower’s, pension is paid to the widow or widower of the deceased based on the social security contributions made by their deceased spouse. It is less than a retirement pension and normally amounts to 52% of the deceased’s regulatory base, although it can be higher and even be as much as 70% in very exceptional cases.
This pension is compatible with the normal retirement pension and is paid indefinitely.
To qualify for it, both the person receiving the benefit and the person who generated it must meet a series of requirements.
An orphan’s pension is paid to children under 21 years of age who have been orphaned, although it can be extended to 25 years of age if they earn less than the minimum wage. Again, it is also necessary for the parents to have met a series of requirements, and they must have paid a minimum number of years of Social Security contributions. That is why we talk about a contributory pension.
Contributory pension for permanent disability
The Social Security also covers people who are unable to work due to some type of disability.
This type of state payment can be partial, permanent total or absolute depending on the person’s degree of incapacity in terms of carrying out either the work that was being performed or any other work.
Total permanent disability is where the person is unable to carry out their usual activity, and absolute disability is where the person is unable to carry out any type of work activity at all.
A disability pension and a retirement pension are incompatible when they come from the same Social Security system. Therefore, when they reach retirement age the person will receive their retirement pension, although it is also possible to maintain the amount of the disability payments if these were higher.
Childbirth and childcare benefit
This contributory benefit is what is known as the maternity or paternity benefit. It is the money that Social Security pays for 16 weeks to mothers for the birth or adoption of children.
The amount of this benefit or subsidy is 100% of the regulatory base of the person’s employment contract.
SOVI pensions
SOVI [from the Spanish Seguro Obligatorio por Vejez e Invalidez] or Compulsory Old Age and Disability Insurance pensions are a relic from the old Social Security regime.
This residual scheme can be applied for by individuals who are not entitled to a pension under the current system and it includes old age, disability and widow’s/widower’s pensions.
Non-contributory pensions
As its name indicates, these types of pensions are not linked to Social Security contributions. They are benefits for people who lack resources and who need a minimum level of protection.
In order to receive this type of benefit, you must prove that your income is below a certain threshold, which is published each year in the Budget Law. These limits increase when you live with other people, although the income of the entire cohabitation unit is taken into account in the calculation.
Non-contributory pensions are managed by each Autonomous Community and by the IMSERSO in Ceuta and Melilla.
As in the previous case, there are several types of non-contributory pensions.
Requirements for applying for a non-contributory disability pension
This benefit is paid to individuals between 18 and 65 years of age who have a disability of more than 65% and who have resided in Spain for at least five years, two of which must have been immediately prior to the application.
Non-contributory retirement pension
This pension can be received when the person has not paid in to the system for the 15 years required to receive a contributory pension.
To apply for it, you must have reached retirement age and prove that you do not have sufficient income.


